Detailed Description
The core functions provide the direct interface to the CAN controller (hardware). Please note that due to hardware limitations certain functions may not be implemented on the target platform. A call to an unsupported function will always return the error code eCP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED.
For a "Full CAN" controller (i.e. a CAN controller that has several message buffers) an extended set of powerful functions (CpCoreBuffer..()) is provided.
Initialisation Process
The CAN driver is initialised with the function CpCoreDriverInit(). This routine sets up the CAN controller, but does not configure a specific bit rate, nor switch the CAN controller to active operation. The following core functions must be called in that order:
The function CpCoreDriverInit() must be called before any other core function in order to have a valid handle / pointer to the open CAN interface.
Example
Driver Configuration
Each CANpie FD driver is individually configured, the CANpie FD configuration options are defined inside the cp_platform.h file.
#include "cp_fifo.h"Functions | |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreBitrate (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, int32_t slNomBitRateV, int32_t slDatBitRateV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreBufferConfig (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV, uint32_t ulIdentifierV, uint32_t ulAcceptMaskV, uint8_t ubFormatV, uint8_t ubDirectionV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreBufferGetData (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV, uint8_t *pubDestDataV, uint8_t ubStartPosV, uint8_t ubSizeV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreBufferGetDlc (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV, uint8_t *pubDlcV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreBufferRelease (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreBufferSend (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreBufferSetData (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV, uint8_t *pubSrcDataV, uint8_t ubStartPosV, uint8_t ubSizeV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreBufferSetDlc (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV, uint8_t ubDlcV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreCanMode (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubModeV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreCanState (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, CpState_ts *ptsStateV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreDriverInit (uint8_t ubPhyIfV, CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubConfigV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreDriverRelease (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreFifoConfig (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV, CpFifo_ts *ptsFifoV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreFifoRead (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV, CpCanMsg_ts *ptsCanMsgV, uint32_t *pulMsgCntV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreFifoRelease (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreFifoWrite (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV, CpCanMsg_ts *ptsCanMsgV, uint32_t *pulMsgCntV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreHDI (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, CpHdi_ts *ptsHdiV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreIntFunctions (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, CpRcvHandler_Fn pfnRcvHandlerV, CpTrmHandler_Fn pfnTrmHandlerV, CpErrHandler_Fn pfnErrHandlerV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreStatistic (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV, CpStatistic_ts *ptsStatsV) |
| CpStatus_tv | CpCoreStatisticClear (CpPort_ts *ptsPortV) |
Function Documentation
◆ CpCoreBitrate()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreBitrate | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| int32_t | slNomBitRateV, | ||
| int32_t | slDatBitRateV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] slNomBitRateV Nominal bit-timing selection [in] slDatBitRateV Data bit-timing selection
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function initialises the bit-timing registers of a CAN controller to predefined values. The values are defined by the enumeration CpBitrate_e. For a Classic CAN controller (or if bit rate switching is not required), set the parameter slDatBitRateV to eCP_BITRATE_NONE.
◆ CpCoreBufferConfig()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreBufferConfig | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV, | ||
| uint32_t | ulIdentifierV, | ||
| uint32_t | ulAcceptMaskV, | ||
| uint8_t | ubFormatV, | ||
| uint8_t | ubDirectionV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number [in] ulIdentifierV Identifier value [in] ulAcceptMaskV Acceptance mask value [in] ubFormatV Frame format [in] ubDirectionV Frame direction
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
- See also
- CpCoreBufferRelease()
This function allocates a message buffer in a CAN controller. The number of the message buffer inside the CAN controller is denoted via the parameter ubBufferIdxV. The first buffer starts at position eCP_BUFFER_1. The message buffer is allocated with the identifier value ulIdentifierV. If the buffer is used for reception (parameter ubDirectionV is eCP_BUFFER_DIR_RCV), the parameter ulAcceptMaskV is used for acceptance filtering.
The parameter ubFormatV can have the following values:
- CP_MSG_FORMAT_CBFF : Classic CAN frame, Standard Identifier
- CP_MSG_FORMAT_CEFF : Classic CAN frame, Extended Identifier
- CP_MSG_FORMAT_FBFF : ISO CAN FD frame, Standard Identifier
- CP_MSG_FORMAT_FEFF : ISO CAN FD frame, Extended Identifier
The following example shows the set-up of a transmit buffer
An allocated transmit buffer can be sent using the function CpCoreBufferSend().
The function initialises the DLC value of a message buffer to 0; a subsequent call to CpCoreBufferSetDlc() is necessary to change the default value.
◆ CpCoreBufferGetData()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreBufferGetData | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV, | ||
| uint8_t * | pubDestDataV, | ||
| uint8_t | ubStartPosV, | ||
| uint8_t | ubSizeV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number [out] pubDestDataV Pointer to destination data buffer [in] ubStartPosV Array start position [in] ubSizeV Number of bytes to read
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
The function copies ubSizeV data bytes from the CAN message buffer defined by ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. The parameter ubStartPosV denotes the start position, the first data byte is at position 0. The destination buffer (pointer pubDestDataV) must have sufficient space for the data. The buffer has to be configured by CpCoreBufferConfig() in advance.
◆ CpCoreBufferGetDlc()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreBufferGetDlc | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV, | ||
| uint8_t * | pubDlcV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number [out] pubDlcV Data Length Code
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function retrieves the Data Length Code (DLC) of the selected buffer ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. The parameter pubDlcV is a pointer to a memory location where the function will store the DLC value on success. The buffer has to be configured by CpCoreBufferConfig() in advance.
◆ CpCoreBufferRelease()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreBufferRelease | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
- See also
- CpCoreBufferConfig()
The function releases the allocated message buffer specified by the parameter ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. Afterwards, both reception and transmission are disabled on the specified message buffer.
◆ CpCoreBufferSend()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreBufferSend | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Index of message buffer
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function transmits a CAN frame from the specified message buffer ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. The message buffer has to be configured as transmit buffer (eCP_BUFFER_DIR_TRM) by a call to CpCoreBufferConfig() in advance. A transmission request on a receive buffer will fail with the return code eCP_ERR_INIT_FAIL.
◆ CpCoreBufferSetData()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreBufferSetData | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV, | ||
| uint8_t * | pubSrcDataV, | ||
| uint8_t | ubStartPosV, | ||
| uint8_t | ubSizeV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number [in] pubSrcDataV Pointer to source data buffer [in] ubStartPosV Array start position [in] ubSizeV Number of bytes to write
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function copies ubSizeV data bytes from the source buffer (pointer pubSrcDataV) into the message buffer defined by the parameter ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. The parameter ubStartPosV denotes the start position, the first data byte is at position 0. The message buffer has to be configured by CpCoreBufferConfig() in advance.
The following example demonstrates the access to the data bytes of a CAN frame:
◆ CpCoreBufferSetDlc()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreBufferSetDlc | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV, | ||
| uint8_t | ubDlcV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number [in] ubDlcV Data Length Code
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function sets the Data Length Code (DLC) of the specified message buffer ubBufferIdxV. The DLC value ubDlcV must be in the range from 0 to 8 for Classic CAN frames and 0 to 15 for ISO CAN FD frames. An invalid DLC value is rejected with the return value eCP_ERR_CAN_DLC. The message buffer has to be configured by a call to CpCoreBufferConfig() in advance.
◆ CpCoreCanMode()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreCanMode | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubModeV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubModeV Mode selection
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
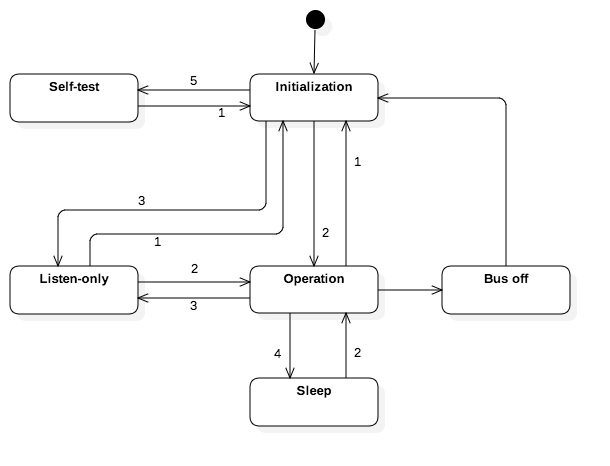
This function changes the operating mode of the CAN controller FSA. Possible values for the parameter ubModeV are defined in the CpMode_e enumeration. At least the modes eCP_MODE_INIT and eCP_MODE_OPERATION shall be supported. Other modes depend on the capabilities of the CAN controller.
◆ CpCoreCanState()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreCanState | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| CpState_ts * | ptsStateV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [out] ptsStateV Pointer to CAN state structure
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function retrieves the present state of the CAN controller. The parameter ptsStateV is a pointer to a memory location where the function will store the state. The value of the structure element CpState_ts::ubCanErrState is defined by the CpState_e enumeration. The value of the structure element CpState_ts::ubCanErrType is defined by the CpErrType_e enumeration.
◆ CpCoreDriverInit()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreDriverInit | ( | uint8_t | ubPhyIfV, |
| CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, | ||
| uint8_t | ubConfigV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ubPhyIfV CAN channel of the hardware [out] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubConfigV This parameter is reserved for future enhancement
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
- See also
- CpCoreDriverRelease()
The function opens the physical CAN interface defined by the parameter ubPhyIfV. The value for ubPhyIfV is taken from the enumeration CpChannel_e. The function sets up the field members of the CAN port structure CpPort_ts. The parameter ptsPortV is a pointer to a memory location where the structure CpPort_ts is stored. An opened CAN port must be closed via the CpCoreDriverRelease() function.
◆ CpCoreDriverRelease()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreDriverRelease | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV | ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
- See also
- CpCoreDriverInit()
The function closes a CAN port. The parameter ptsPortV is a pointer to a memory location where structure CpPort_ts is stored. The implementation of this function is dependent on the operating system. Typical tasks might be:
- clear the interrupt vector / routine
- close all open paths to the hardware
◆ CpCoreFifoConfig()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreFifoConfig | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV, | ||
| CpFifo_ts * | ptsFifoV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number [in] ptsFifoV Pointer to FIFO structure
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function assigns a FIFO to a message buffer defined by the parameter ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. The buffer has to be configured by CpCoreBufferConfig() in advance. The parameter ptsFifoV is a pointer to a memory location where a FIFO has been initialised using the CpFifoInit() function.
The following example shows the configuration of a receive FIFO
◆ CpCoreFifoRead()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreFifoRead | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV, | ||
| CpCanMsg_ts * | ptsCanMsgV, | ||
| uint32_t * | pulMsgCntV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number [out] ptsCanMsgV Pointer to a CAN frame structure [in,out] pulMsgCntV Pointer to CAN frame counter variable
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function reads CAN frames from a receive FIFO defined by the parameter ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. The FIFO has to be configured by CpCoreFifoConfig() in advance. The parameter ptsCanMsgV is a pointer to the application buffer as array of CpCanMsg_ts objects to store the received CAN frames. The parameter pulMsgCntV is a pointer to a memory location that must be initialised before the call with the capacity (number of CpCanMsg_ts elements) of the buffer referenced by ptsCanMsgV. Upon return, the driver stores the number of CAN frames copied into the application buffer in this parameter.
The following example shows a read operation from a receive FIFO
◆ CpCoreFifoRelease()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreFifoRelease | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function releases an assigned FIFO from a message buffer defined by the parameter ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. The FIFO has to be configured by CpCoreFifoConfig() in advance.
◆ CpCoreFifoWrite()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreFifoWrite | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| uint8_t | ubBufferIdxV, | ||
| CpCanMsg_ts * | ptsCanMsgV, | ||
| uint32_t * | pulMsgCntV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ubBufferIdxV Buffer number [in] ptsCanMsgV Pointer to a CAN frame structure [in,out] pulMsgCntV Pointer to CAN frame counter variable
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function writes CAN frames to a transmit FIFO defined by the parameter ubBufferIdxV. The first message buffer starts at the index eCP_BUFFER_1. The FIFO has to be configured by CpCoreFifoConfig() in advance. The parameter ptsCanMsgV is a pointer to the application buffer as array of CpCanMsg_ts objects which contain the CAN frames that should be transmitted. The parameter pulMsgCntV is a pointer to a memory location that must be initialised before the call with the capacity (number of CpCanMsg_ts elements) of the buffer referenced by ptsCanMsgV. Upon return, the driver stores the number of CAN frames transmitted successfully in this parameter.
◆ CpCoreHDI()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreHDI | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| CpHdi_ts * | ptsHdiV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [out] ptsHdiV Pointer to the Hardware Description Interface structure (CpHdi_ts)
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function retrieves information about the CAN interface. The parameter ptsHdiV is a pointer to a memory location where the function will store the information.
◆ CpCoreIntFunctions()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreIntFunctions | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| CpRcvHandler_Fn | pfnRcvHandlerV, | ||
| CpTrmHandler_Fn | pfnTrmHandlerV, | ||
| CpErrHandler_Fn | pfnErrHandlerV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] pfnRcvHandlerV Pointer to callback function for receive handler [in] pfnTrmHandlerV Pointer to callback function for transmit handler [in] pfnErrHandlerV Pointer to callback function for error handler
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function installs three different callback routines in the interrupt handler. If you do not want to install a callback for a certain interrupt condition, set the parameter to NULL. The callback functions for receive and transmit interrupts have the following syntax: uint8_t Handler(CpCanMsg_ts * ptsCanMsgV, uint8_t ubBufferIdxV)
The callback function for the CAN status-change / error interrupt has the following syntax: uint8_t Handler(CpState_ts * ptsErrV)
◆ CpCoreStatistic()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreStatistic | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV, |
| CpStatistic_ts * | ptsStatsV ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure [in] ptsStatsV Pointer to statistics data structure
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function copies CAN statistics information to the structure pointed to by ptsStatsV.
◆ CpCoreStatisticClear()
| CpStatus_tv CpCoreStatisticClear | ( | CpPort_ts * | ptsPortV | ) |
- Parameters
-
[in] ptsPortV Pointer to CAN port structure
- Returns
- Error code is defined by the CpErr_e enumeration. If no error occurred, the function will return the value
eCP_ERR_NONE.
This function clears CAN controller statistics.